Do you know the difference between CRM and CXM and how they can help propel your business?
As a marketer or business owner, you probably hear the words CRM vs CXM being thrown around a lot.
These are terms that describe the strategies and technologies used for managing an organization’s interaction with its customers, both current and potential.
For example, by focusing on marketing strategy, sales analysis, and technical support, businesses were able to comprehend who their customers were. This would help make the sales efforts directed toward those customers seem more relevant.
The first step is to create a platform for interaction using CRM for managing customer relationships. The next step is Customer Experience Management (CXM) which helps to understand as well as influence customer perceptions regarding a business and its products at the various touch points of the customer journey.
Let us discuss comprehensively the difference between CX vs CRM, its meaning, and key use cases.
What is Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer relationship management (CRM) is defined as a strategy that focuses on building and strengthening relationships between businesses and their customers.
CRM software is used to track customer interactions, manage sales processes, and automate processes that improve the customer experience. CRM strategies aim to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, increase sales and retention rates, and reduce customer churn.
What is Customer Experience Management (CXM)?
Customer experience management (CXM) refers to the practice of managing interactions between businesses and their customers in a way that creates a positive and satisfactory customer experience.
CXM takes a holistic approach to managing customer interactions, aiming to provide a seamless and consistent experience across all channels and touchpoints, from the first point of contact to post-purchase follow-up.
How do CRM and CXM Work Together?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Customer Experience Management (CXM) are two important concepts that businesses need to understand in order to be successful.
CRM refers to the strategies, technologies, and practices that companies use to manage, analyze, and improve interactions with customers. Meanwhile, CXM is the practice of designing and managing interactions between a business and its customers in order to achieve a positive customer experience.

But how do these two concepts work together?
Let’s dive deeper into how CRM and CXM can complement each other.
1. Collecting Customer Data
Both CRM and CXM solutions start with collecting customer data. A CRM system is responsible for collecting customer transactions, communication, and demographic data.
The collected data will be used to manage customer relationships and design effective marketing strategies.
On the other hand, CXM collects customer feedback, preferences, and satisfaction data to improve customer engagement and satisfaction. Both sets of data are complementary and can be used together to create a more comprehensive picture of the customer.
2. Analyzing Customer Data
Customer data analysis is a very crucial part as it directly impacts the success rate of the strategies designed for customer management.
After the data is collected, CRM and CXM analytics assess customer behavior, preferences, and feedback. Analytics can help companies in the following areas:
- Identify latest trends
- Know the patterns customers are following
- Spot the areas of improvement
By depending on the same customer data, CXM and CRM analytics can complement each other and work in sync to provide a holistic view of the customer.
3. Personalizing Customer Experience
Personalization is always in vogue when it comes to delivering excellent customer experience.
By performing thorough data analysis, companies can personalize customer interactions, offering relevant content, and services. CRM helps to personalize and automate targeted campaigns based on customer preferences and behavior.
CXM, on the other hand, brings a more contextualized approach to customization, using customer feedback and touchpoints to offer a more personal, empathic customer experience.
It’s important for companies to balance their efforts in this area by using the data from CRM and CXM to provide a personalized customer journey.
4. Engaging Customers Across Channels
Interaction consistently across all communication channels that your customers prefer to connect with your company is extremely crucial.
CRM platforms help businesses efficiently engage with customers via multiple channels such as email, phone, and social media. CXM, however, offers a more immersive and seamless engagement experience, ensuring that customers’ journeys across channels are consistent and connected.
Working together, CRM and CXM can improve the quality and frequency of customer touchpoints, allowing for better communication and engagement.
5. Building Long-Term Relationships
Ultimately, the goal of both CRM and CXM is to build long-term, sustainable relationships with customers.
CRM systems help companies manage the customer journey while CXM ensures that that journey is positive, memorable, and engaging.
By working together, or as part of a unified strategy, businesses are more likely to build strong, loyal relationships with customers that benefit both the customer and business alike.
Key Differences Between CXM vs CRM
While CXM and CRM share some similarities, they have different scopes, objectives, and focuses. Understanding the differences between CXM and CRM can help businesses know which approach to take in improving their customer experience and engagement.
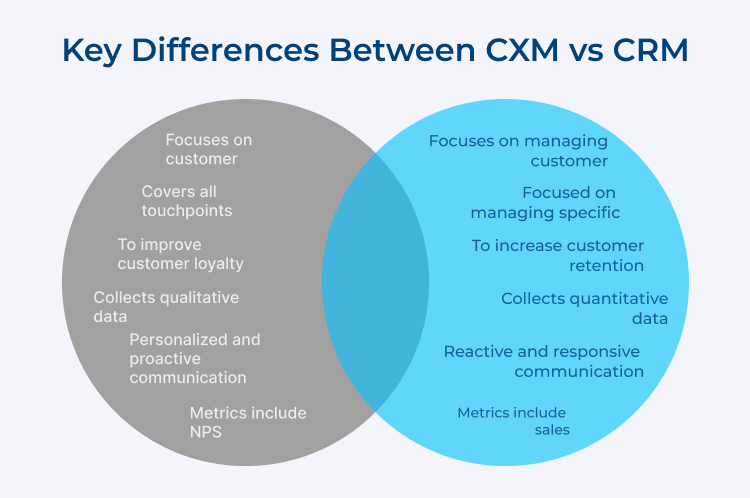
A combination of both CXM and CRM strategies can reinforce customer loyalty and drive business success.
| Type of Difference |
Customer Experience Management (CEM) |
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) |
| Focus |
Focuses on customer experience and satisfaction |
Focuses on managing customer relationships and interactions |
| Scope |
Covers all touchpoints of the customer journey |
Focused on managing specific touchpoints |
| Objective |
To improve customer loyalty and retention |
To increase customer retention and revenue |
| Data Collection |
Collects qualitative data and feedback |
Collects quantitative data and customer details |
| Communication |
Personalized and proactive communication |
Reactive and responsive communication |
| Metrics |
Metrics include NPS, customer satisfaction, etc. |
Metrics include sales, revenue, and retention |
Focus
CXM (customer experience management) and CRM (customer relationship management) both focus on improving the customer experience, but CXM is overarching, while CRM is more focused. CXM is about understanding the customer journey and providing a tailored, personalized experience at every touchpoint, while CRM is focused on managing and organizing customer information.
Scope
CXM has a wider and broader scope, which means that it involves every aspect of the customer experience, including marketing, sales, customer service, and social media interactions. Meanwhile, CRM is more focused on sales, marketing, and customer service, with customer data management being the central element.
Objective
The objective of CXM is to provide an engaging, personalized experience that addresses the customer’s needs, preferences, and problems – no matter where they are in their journey. In contrast, the primary objective of CRM is to manage customer interactions and data and to streamline business processes through automation and standardization.
Data Collection
For CXM, data collection involves gathering insights into customer behavior from various sources, such as surveys, social media, website analytics, and online reviews, to provide data-driven insights. On the other hand, CRM is focused on capturing and storing customer data related to purchases, interactions, and service requests for business use and analysis.
Communication
CXM aims to engage customers through personalized and relevant communications across various channels such as social media, email, and mobile. It emphasizes building meaningful relationships with customers over the long term. Meanwhile, CRM focuses more on the transactional communication that occurs between the business and customers during the lifecycle of a purchase or service.
Metrics
For CXM, the primary metrics are customer retention, engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty. On the other hand, the metrics for CRM are sales, revenue, customer acquisition, and cost of customer acquisition.
Key Use Cases of Customer Experience Management (CXM)

Let us discuss some important use cases of customer experience management (CXM)
1. Improve Customer Satisfaction
One of the primary goals of CEM is to understand and improve customer satisfaction levels.
By gathering customer feedback, analyzing customer interactions, and identifying pain points and areas for improvement, companies can take targeted actions to enhance the overall customer experience.
It leads to higher levels of customer satisfaction, which can translate into increased loyalty and repeat business.
2. Personalize Customer Interactions
With the rise of digital technologies and social media, customers now expect a personalized experience from the brands they interact with.
CEM can help companies achieve this by collecting data on customer behavior, preferences, and past interactions, and using this information to personalize future interactions.
It could involve tailoring marketing messages, recommending relevant products and services, or providing customized support to each customer.
3. Enhance Brand Reputation
Positive customer experiences can go a long way in building a strong brand reputation. CEM can help companies monitor their online reputation across various platforms, track customer sentiment, and quickly respond to negative feedback.
By demonstrating a commitment to improving the customer experience and resolving issues in a timely manner, companies can win over customers and enhance their brand image.
4. Increase Customer Lifetime Value
CEM can also help companies increase customer lifetime value (CLV) by identifying opportunities to upsell or cross-sell products and services to existing customers.
By analyzing customer data and behavior, companies can identify which customers are most likely to make additional purchases and target them with relevant offers and promotions.
It not only drives additional revenue but also helps deepen the relationship between the customer and the brand.
5. Foster Employee Engagement
CEM can also benefit employees by fostering a customer-centric culture within the organization.
By providing employees with the tools and training they need to deliver exceptional customer experiences, companies can improve employee engagement and retention.
It eventually leads to a more motivated and productive workforce, which can further enhance the customer experience.
Concluding CX vs CRM
Customer Relationship Management software is an important part of any business. However, in the era of digital age, businesses need to consider upgrading to a CXM platform. Customer Experience Management is the next step in customer service, and it can provide your customers with an even better experience than ever before.
The above-mentioned differences between CRM vs CXM and its key use cases showcase how it benefits your business. While adopting robust CRM tools is a great start to managing the early stages of customer relationships during acquisition, adoption it is also imperative in improving customers’ experiences through their journeys with your business and greatly improving digital transformation initiatives.