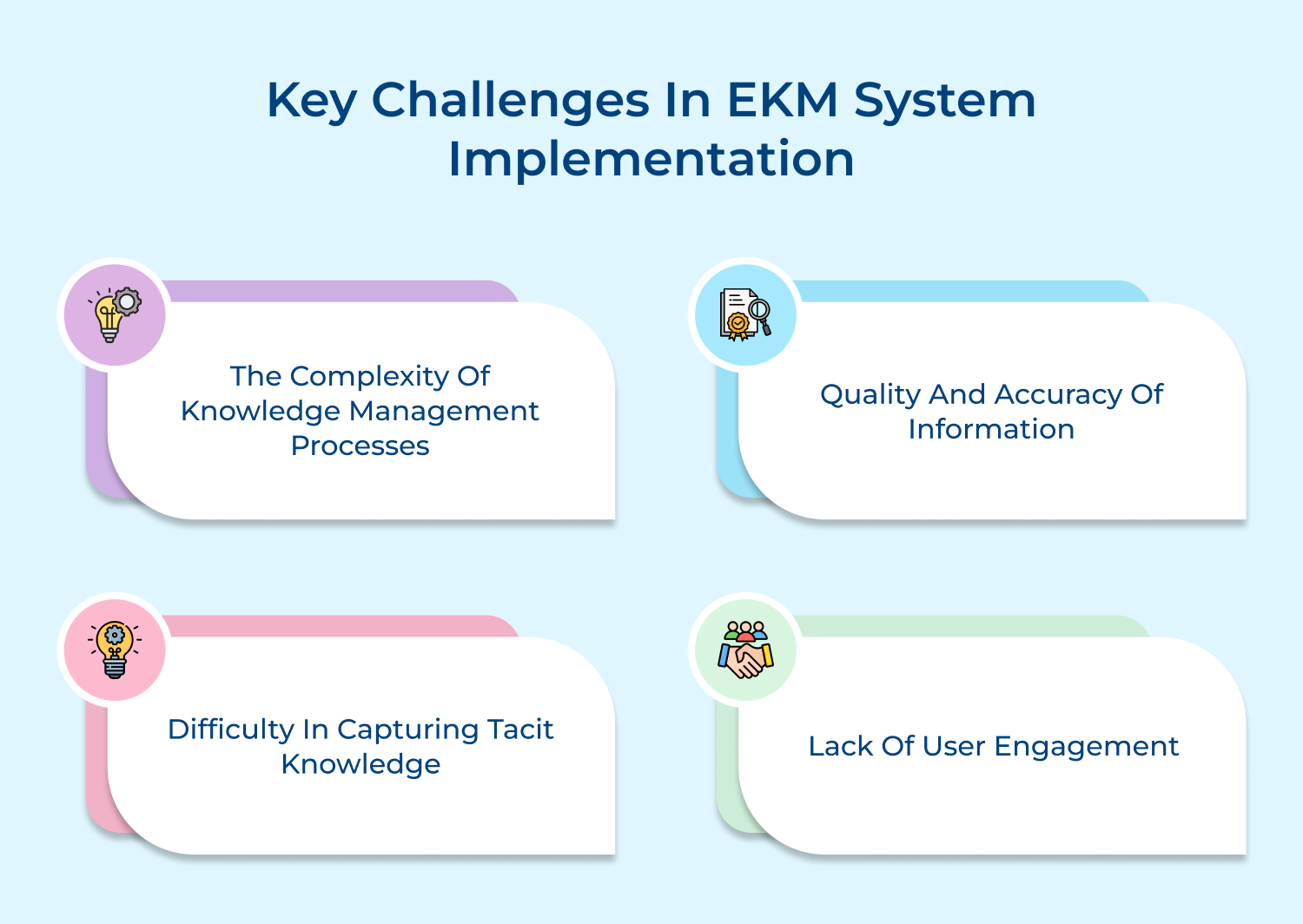
The complexity of Knowledge Management Processes
Challenge: Knowledge management processes can be intricate, involving multiple steps and stakeholders. This complexity can lead to confusion, inconsistency and inefficiency in capturing, organizing, as well as sharing knowledge.
Solution: Simplify and standardize processes where possible. Create clear, step-by-step guidelines for knowledge management activities. Implement user-friendly tools with intuitive interfaces. Provide comprehensive training and support for employees. Use workflow automation to streamline complex processes. Regularly optimize procedures based on user feedback and changing organizational needs.
Quality and Accuracy of Information
Challenge: Ensuring the reliability and relevance of stored information is crucial. Outdated, inaccurate, or irrelevant content can undermine trust in the EKM system while leading to poor decision-making.
Solution: Implement a robust content review and validation process. Assign subject matter experts to verify the information before publication. Establish clear guidelines for content creation and maintenance. Use version control to track changes. Implement a regular content audit schedule to identify and remove outdated information. Encourage user feedback and ratings to help identify accurate content.
Difficulty in Capturing Tacit Knowledge
Challenge: Tacit knowledge, which is often experiential and not easily articulated, can be challenging to capture as well as codify. This type of knowledge is crucial but often lost when experienced employees leave the organization.
Solution: Implement mentoring and knowledge transfer programs to facilitate the sharing of tacit knowledge. Use storytelling and case study methods to capture complex experiences. Utilize video recording for capturing demonstrations of processes. Implement collaborative platforms that allow for informal knowledge exchange. Consider using AI-powered tools for pattern recognition in unstructured data to identify tacit knowledge.
Lack of User Engagement
Challenge: Getting employees to consistently use and contribute to the EKM system can be difficult. Without active participation, the system’s value diminishes and the organization fails to realize the full benefits of knowledge management.
Solution: Create a culture that values and rewards knowledge sharing. Implement gamification elements to make engagement more enjoyable and rewarding. Integrate the EKM system into daily workflows to make its use a natural part of work processes. Provide regular training and support to ensure users are comfortable with the system. Showcase success stories and tangible benefits of using the EKM system. Solicit and act on user feedback to continuously improve the system.
Examples of Enterprise Knowledge Management
EKM is crucial for organizations to capture, organize and leverage their collective knowledge. Here are the examples demonstrating successful EKM implementation across various industries.
1. World Bank’s Knowledge Management Strategy
The World Bank developed a comprehensive KM strategy to improve its development effectiveness. It includes creating Communities of Practice, implementing a robust intranet system and establishing knowledge-sharing events. The strategy focuses on connecting experts across regions, capturing lessons learned from projects and disseminating best practices to enhance the organization’s ability to address global development challenges.
2. Ernst & Young’s Knowledge Web
Ernst & Young developed the Knowledge Web, a global repository of best practices, methodologies and industry insights. The platform enables consultants to access and contribute to the firm’s collective knowledge, improving service delivery as well as client outcomes. The Knowledge Web includes a powerful search engine, discussion forums and expert locator tools, building a culture of continuous innovation.
3. Toyota’s Production System
Toyota’s renowned Production System incorporates knowledge management principles to improve manufacturing processes. The company uses visual management tools, standardized work procedures and regular team meetings to capture knowledge across the organization. The approach has enabled Toyota to maintain its competitive edge in quality and efficiency while creating a culture of continuous improvement.
4. Microsoft’s Knowledge Network
Microsoft implemented a Knowledge Network to connect its vast workforce and facilitate knowledge sharing. The system includes employee profiles, expertise directories and collaboration tools. The Knowledge Network enables employees to find experts quickly, share best practices and collaborate on projects across different departments along with geographical locations. Thus, enhancing innovation and problem-solving capabilities within the company.
5. IBM’s Watson
IBM’s Watson, an AI-powered cognitive computing system, exemplifies advanced enterprise knowledge management. Watson ingests and analyzes vast amounts of structured as well as unstructured data to provide insights, recommendations, etc. In various industries, Watson helps organizations leverage their collective knowledge to improve decision-making, enhance customer service and drive innovation by uncovering patterns that humans might miss.
Maximizing ROI Through Effective KM Practices
Enterprise Knowledge Management is not just a technological initiative, but a strategic approach that can significantly boost an organization’s return on investment. By implementing effective KM practices, businesses can unlock the full potential of their collective knowledge, driving innovation, improving decision-making and enhancing operational efficiency. While challenges exist in implementation, the benefits far outweigh the costs when executed properly.
As organizations continue to navigate an increasingly complex landscape, those who prioritize knowledge management will undoubtedly gain a substantial competitive edge. The key to success lies in viewing KM not as a one-time project, but as an ongoing journey of continuous improvement and adaptation.