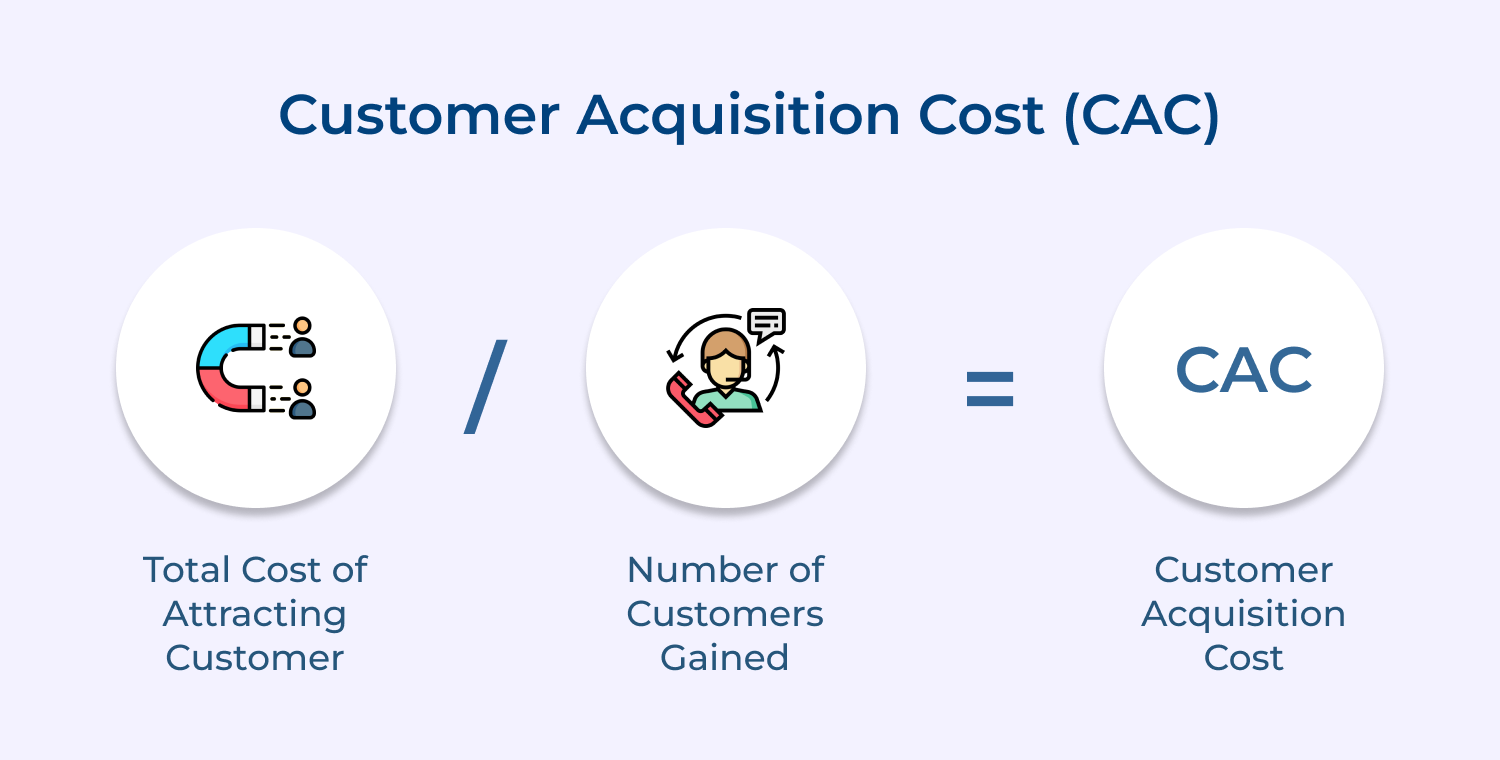
Here’s an example:
Let’s say a company spends $100,000 on sales as well as marketing expenses in a quarter and acquires 100 new customers during that time period. To calculate CAC:
CAC = $100,000 / 100 = $1,000
In example, the CAC is $1,000 per customer.
- Identify all of the costs associated with acquiring new customers, including advertising expenses, sales salaries, bonuses, commissions, lead generation costs, and other expenses related to the sales or marketing process.
- Divide the total cost by the number of new customers acquired during the same period. It will give you the CAC per customer.
- Track CAC over time by repeating the process on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly.
- Compare CAC to other metrics such as Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) and customer retention rate to determine the effectiveness of customer acquisition efforts to identify areas where costs can be reduced.
- Track CAC by segment, this way you can have a clear view of the CAC for different segments of the customer base.
- Use the CAC data to inform your strategy and budget.
CAC can be different for different segments of the customer base, it’s a good idea to calculate it for each of them to have a clear view of the costs in each segment.
6. Churn Rate
Customer churn rate is a metric that measures the rate at which customers are leaving a company. It is typically expressed as a percentage of total customers. A high churn rate can be a sign that a business is not effectively engaging with its customers and retaining them.
Customers that are not engaged with a company may be more likely to leave, which is why customer churn rate is closely related to customer engagement.
To calculate customer churn rate, you can use the following formula:
Churn rate = (Number of customers lost during a period / Total number of customers at the beginning of the period) x 100
A high churn rate can indicate that customers are not satisfied with the products or services provided by the company, or that they are not receiving adequate customer service.
7. Active Users (Monthly or Weekly)
Monthly or Weekly Active Users (MAU or WAU) are metrics that measure the number of unique users who have engaged with a product or service in a given time period, usually a month or a week. These metrics are often used to measure customer engagement in online platforms and mobile apps.
MAU or WAU is an important metric because it provides insights into the level of engagement users have with a product or service. A high number of MAU or WAU can indicate that users are actively and regularly engaging with a product or service, which can be an indication of customer satisfaction as well as loyalty.
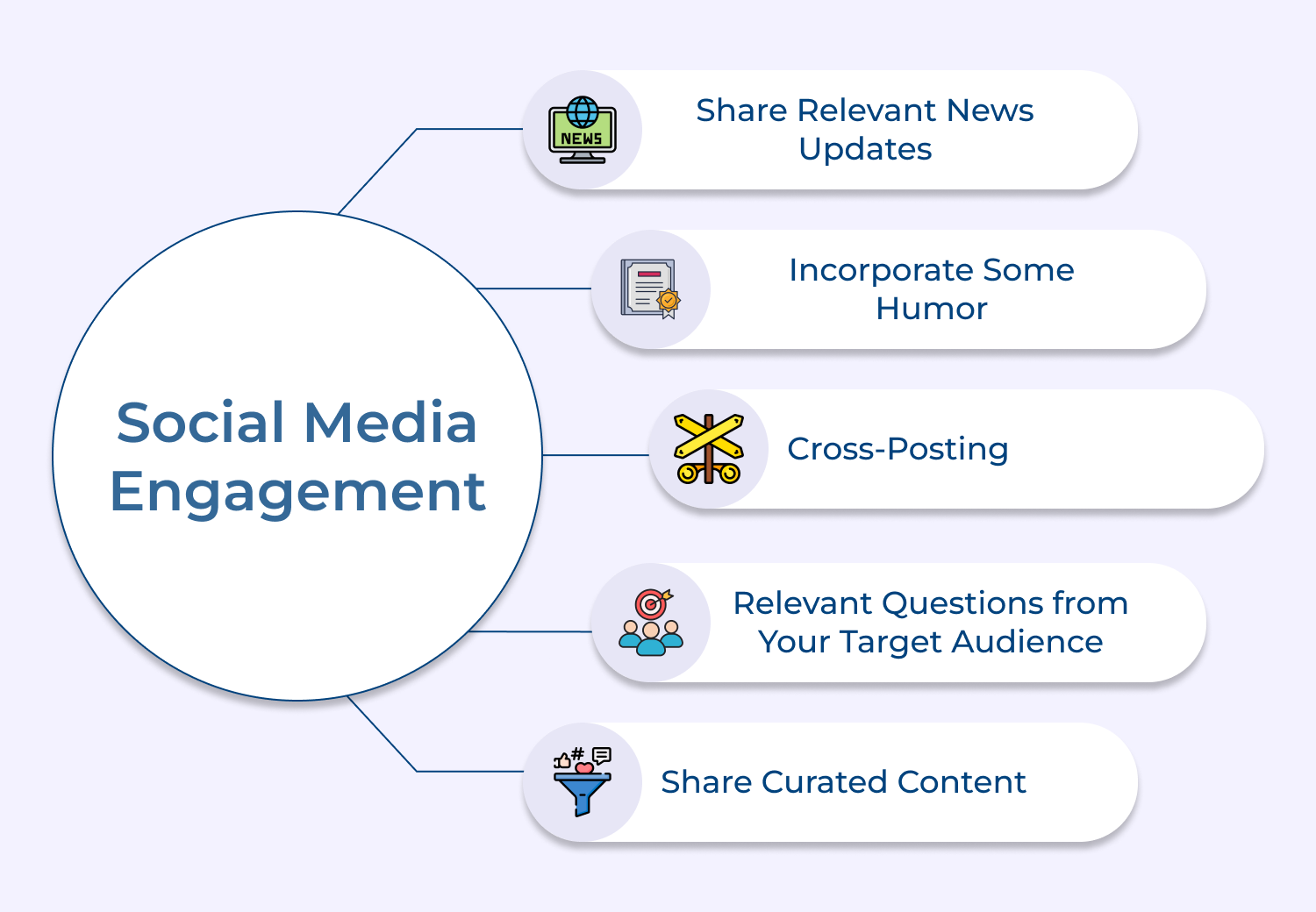
8. Social Media Engagement
Social media engagement is the process of monitoring and analyzing social media conversations to gain insights into customer sentiment, behavior or preferences. Here are some ways to measure customer engagement to improve customer service as well as marketing strategies.