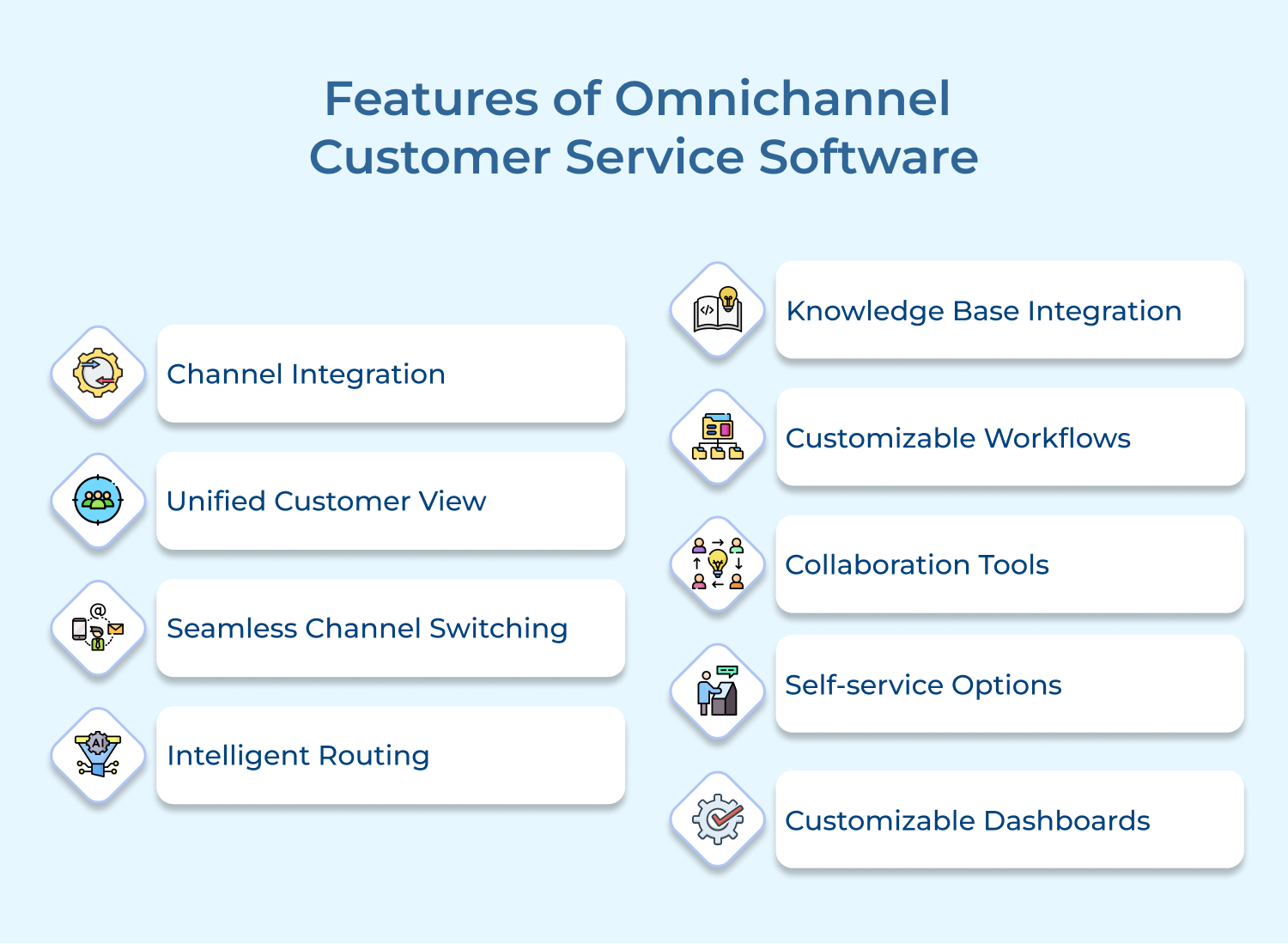
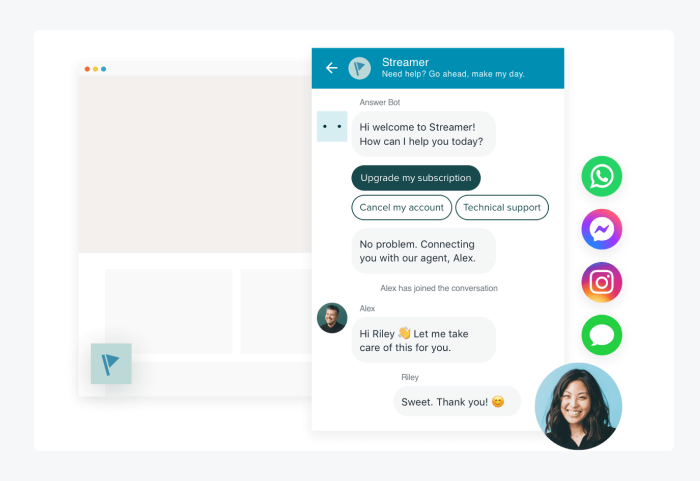
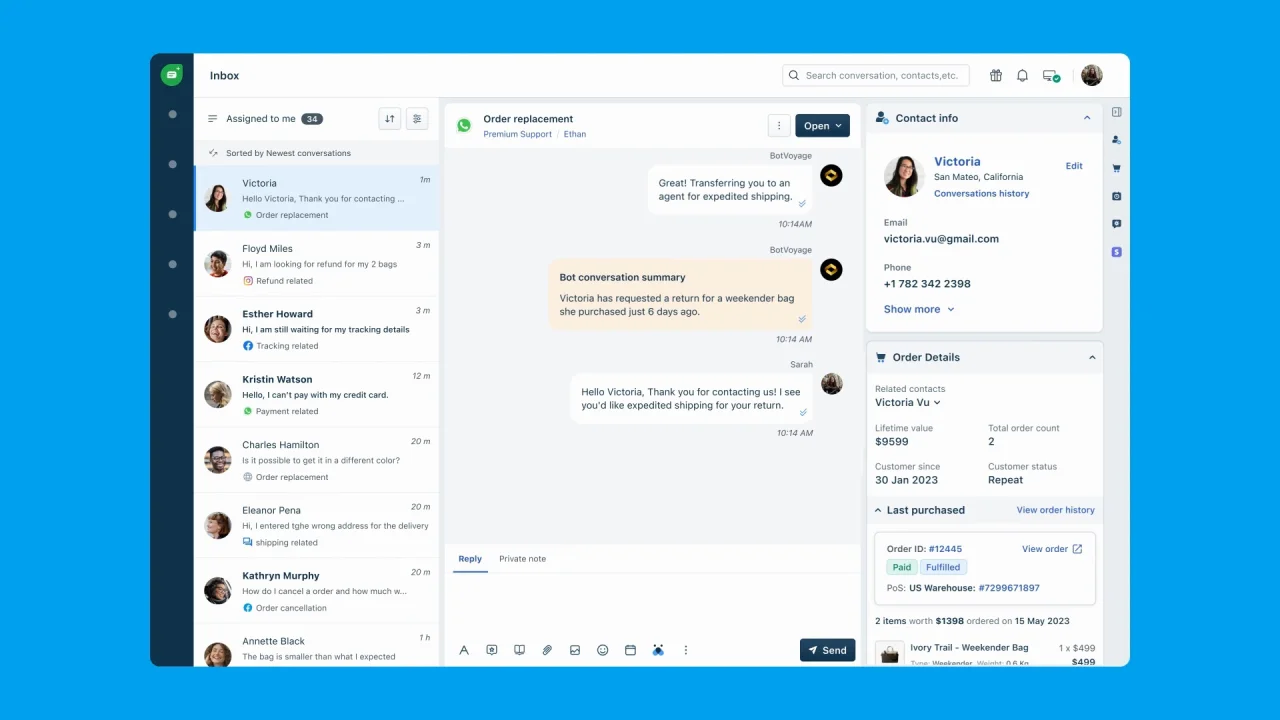
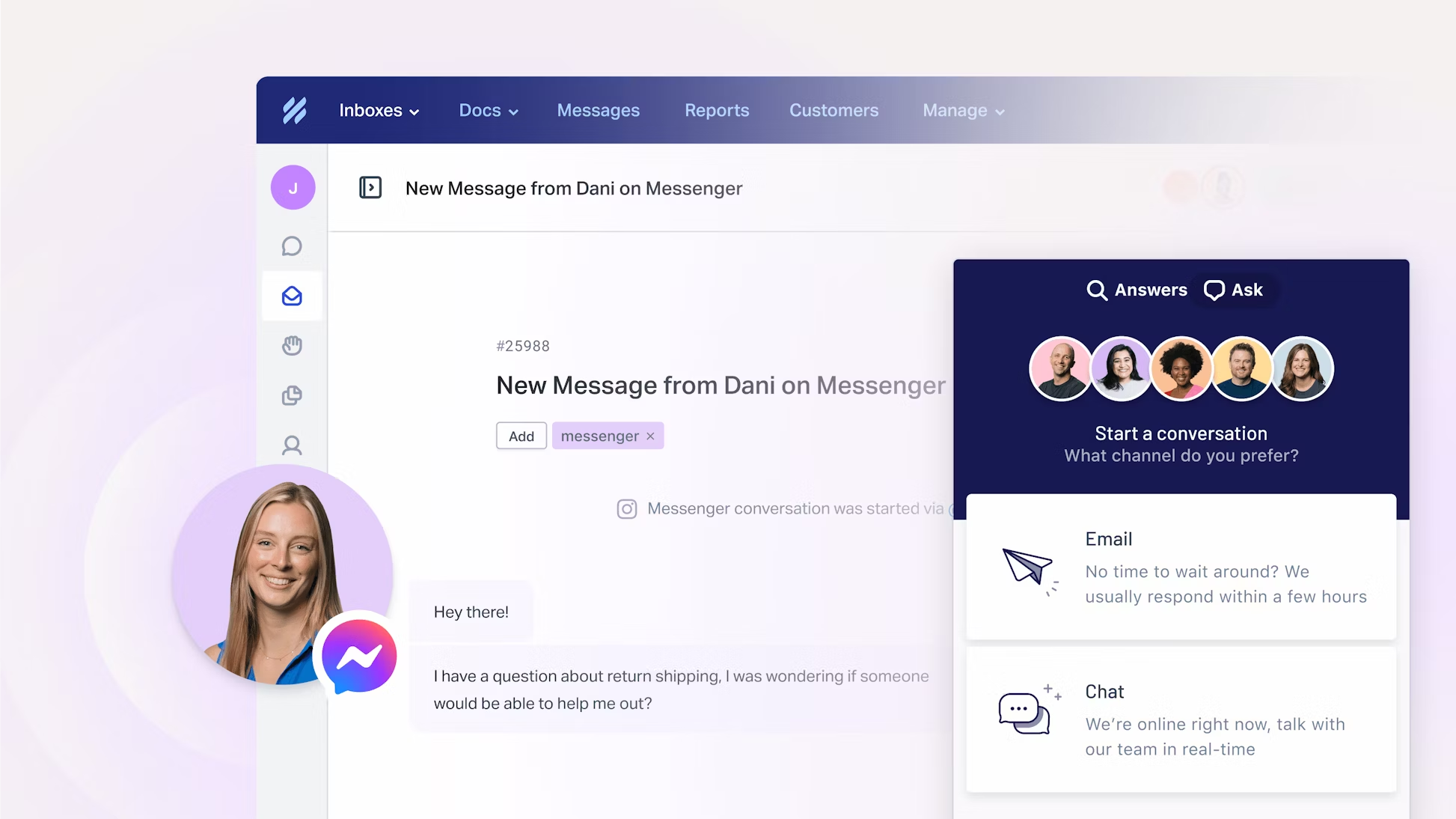
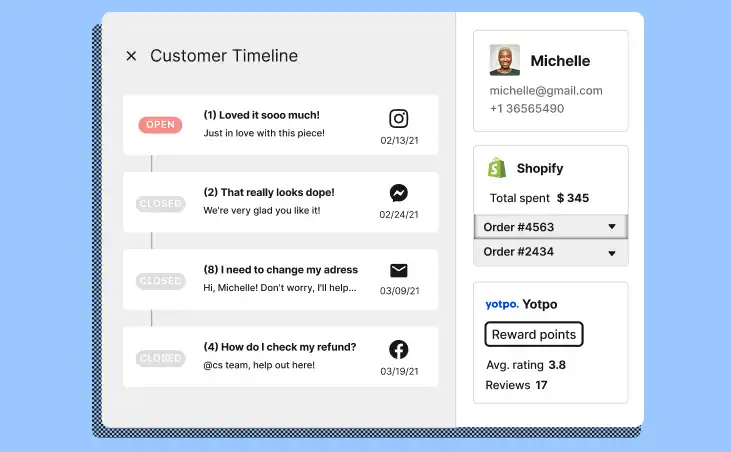
1. Channel Integration
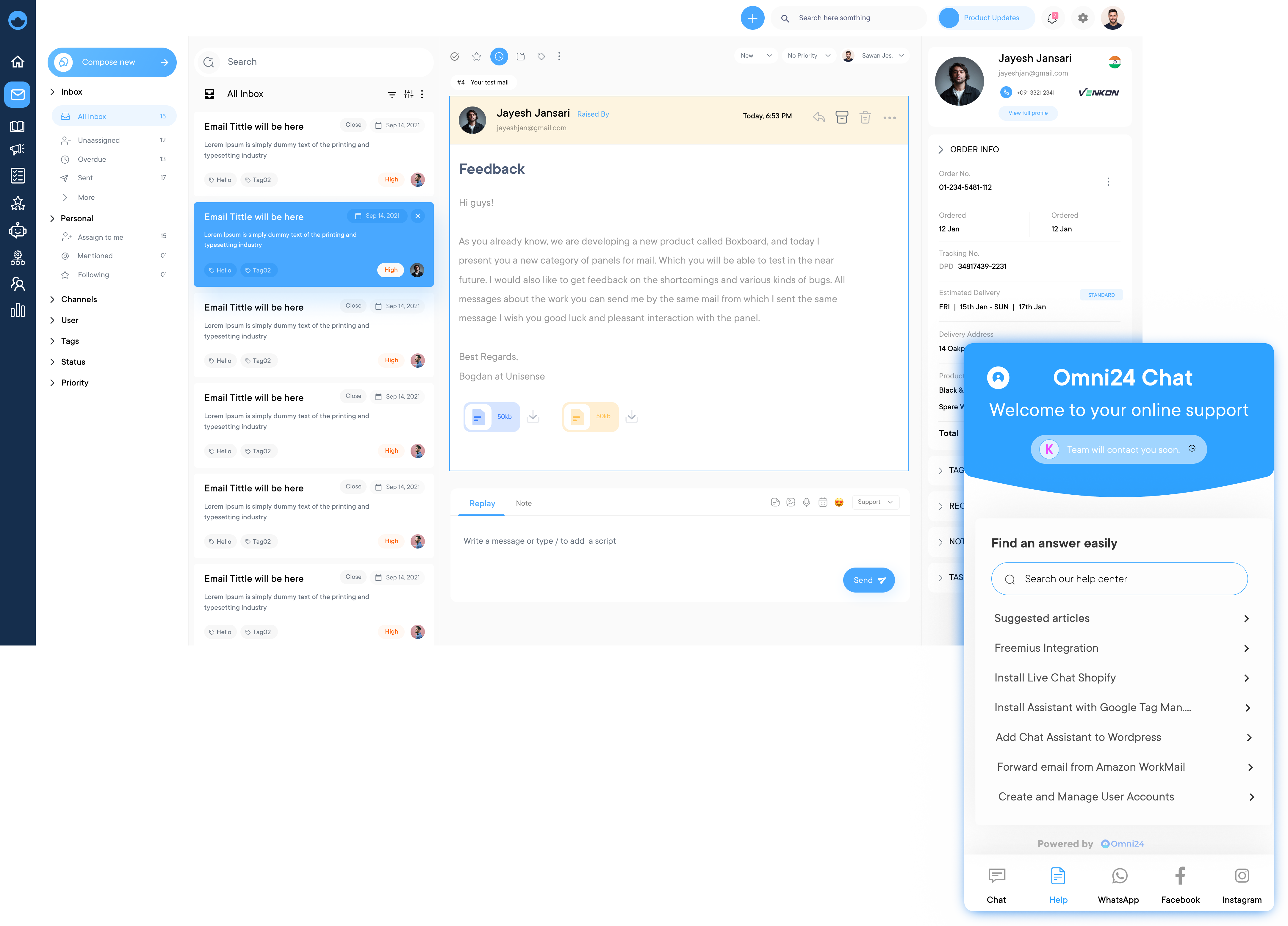
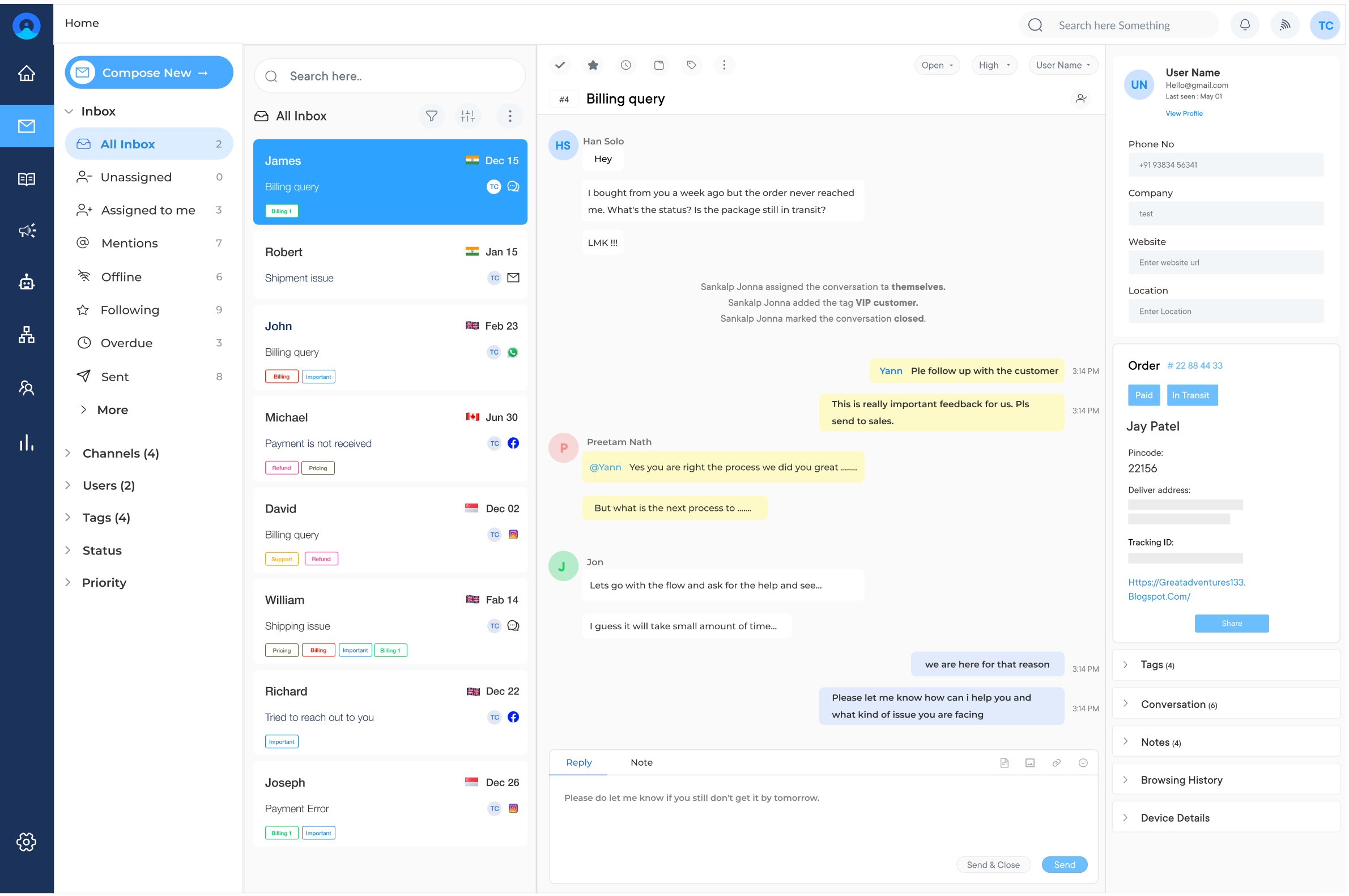
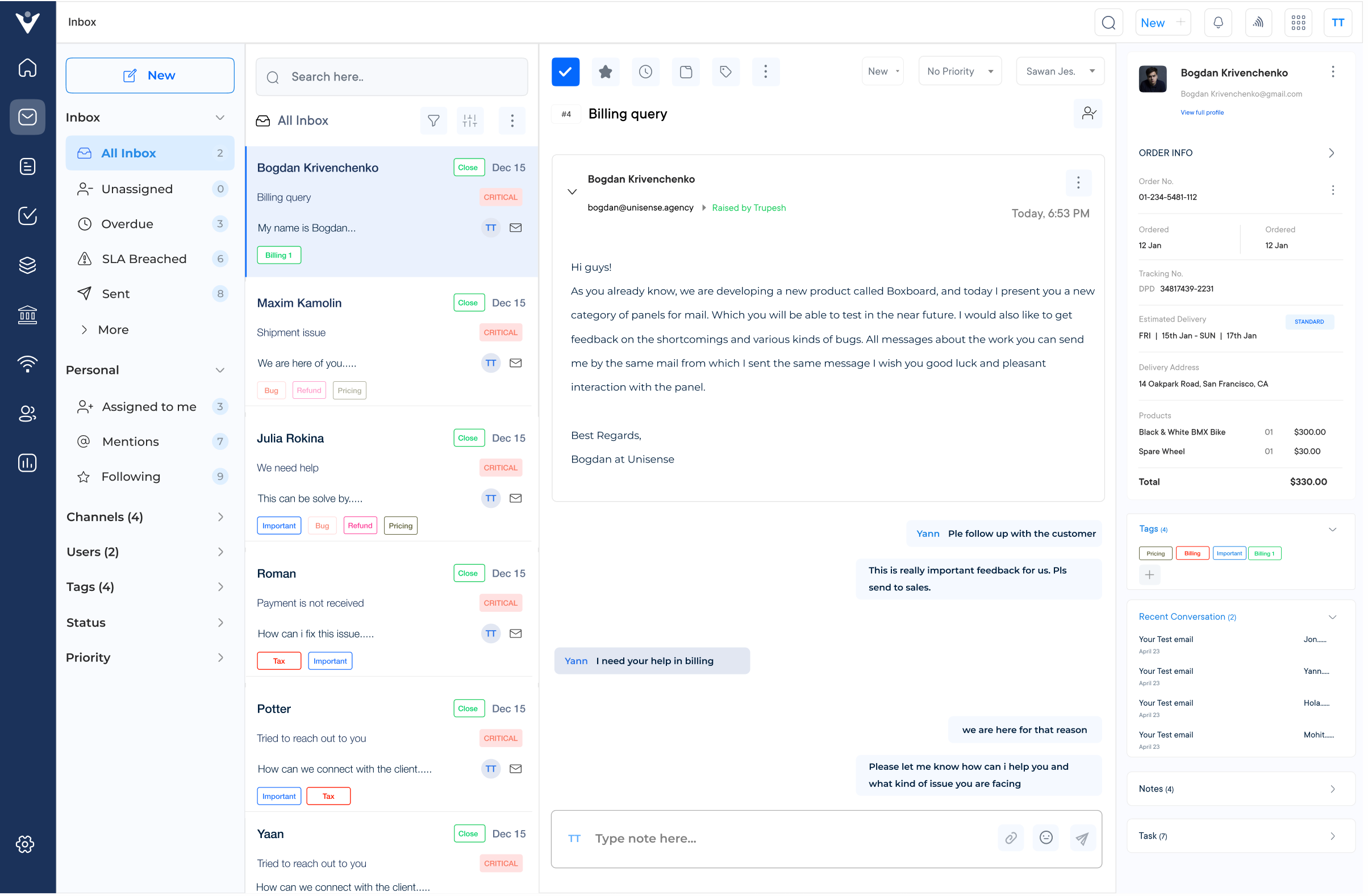
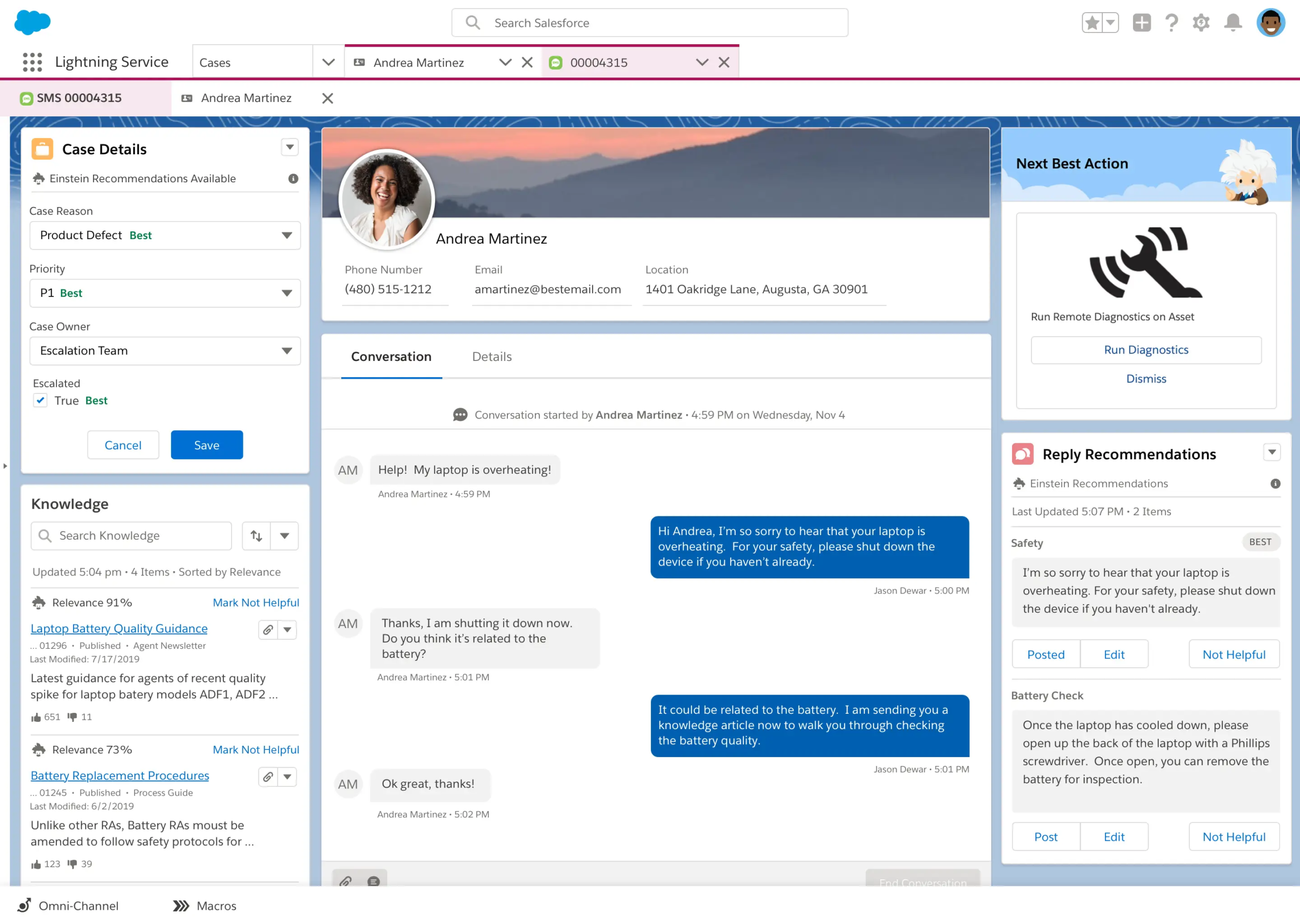
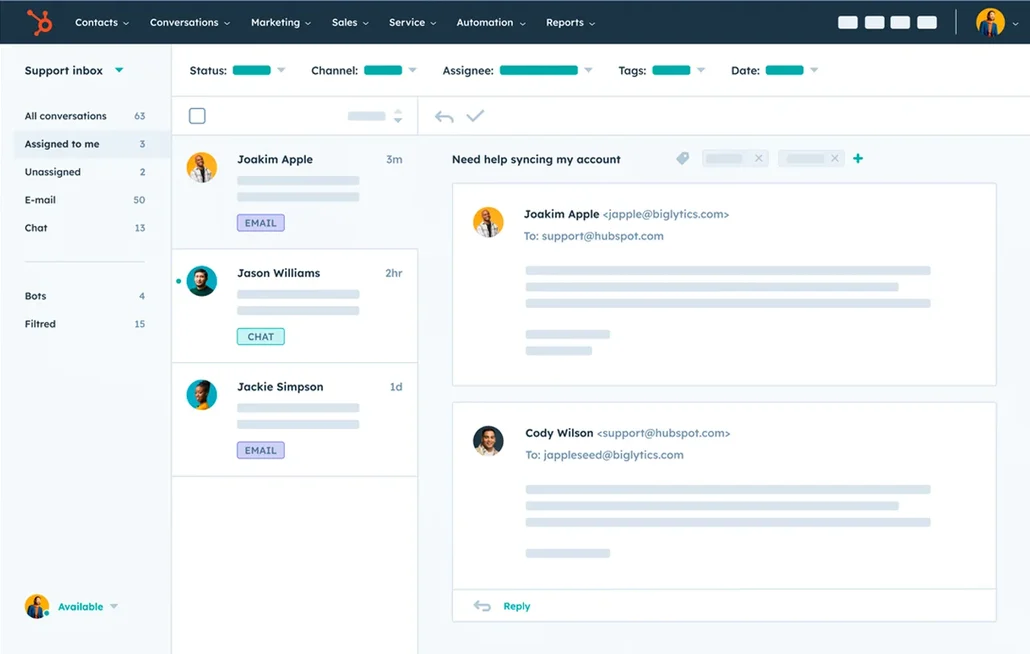
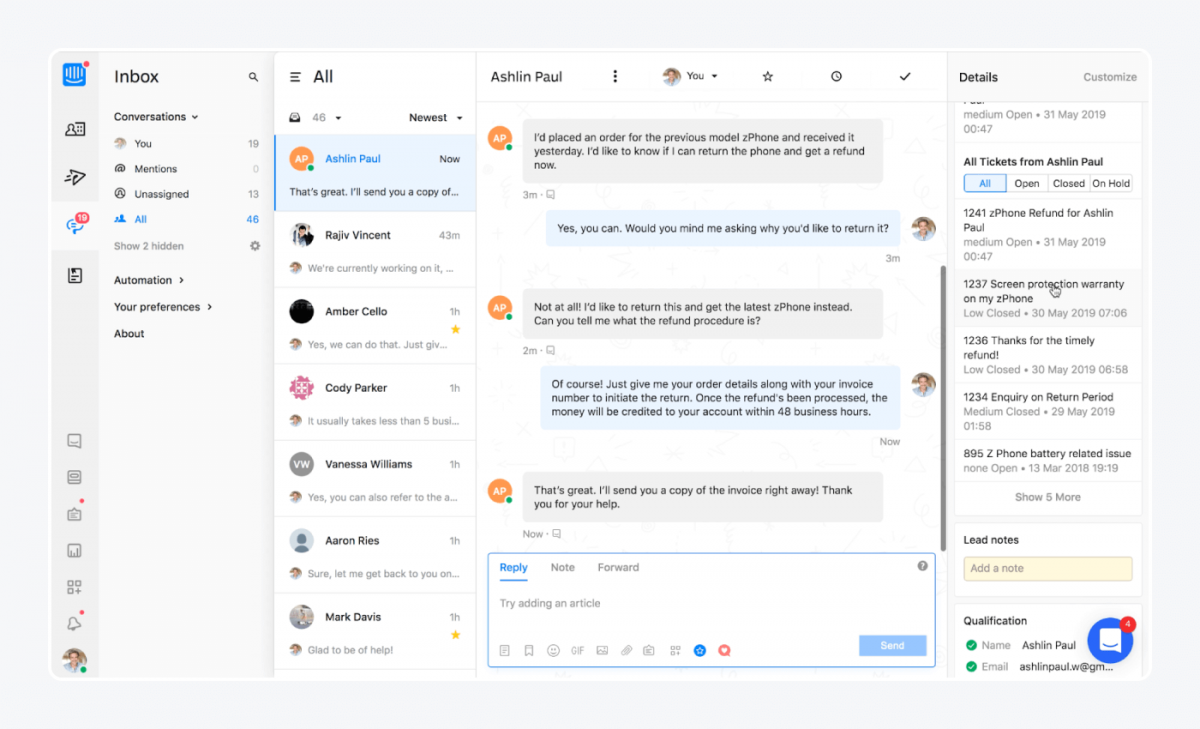
Channel integration is the cornerstone of omnichannel customer service software. It consolidates various communication channels such as phone, email, social media, live chat, and messaging apps into a single platform.
The integration allows businesses to manage all customer interactions from one central hub, ensuring consistency across channels. It eliminates the need for separate systems for each channel, streamlining operations and reducing the risk of miscommunication or lost information. Ultimately, channel integration enables a more cohesive and efficient customer service experience.
2. Unified Customer View
A unified customer view provides a comprehensive, 360-degree perspective of each customer’s history and interactions across all channels. This feature aggregates data from various touchpoints, including purchase history, support tickets, chat logs, and social media interactions.
Agents can quickly understand the customer’s context, preferences, and past issues, leading to more personalized and effective support. The unified approach not only improves the customer experience but also enhances agent efficiency and decision-making capabilities.
3. Seamless Channel Switching
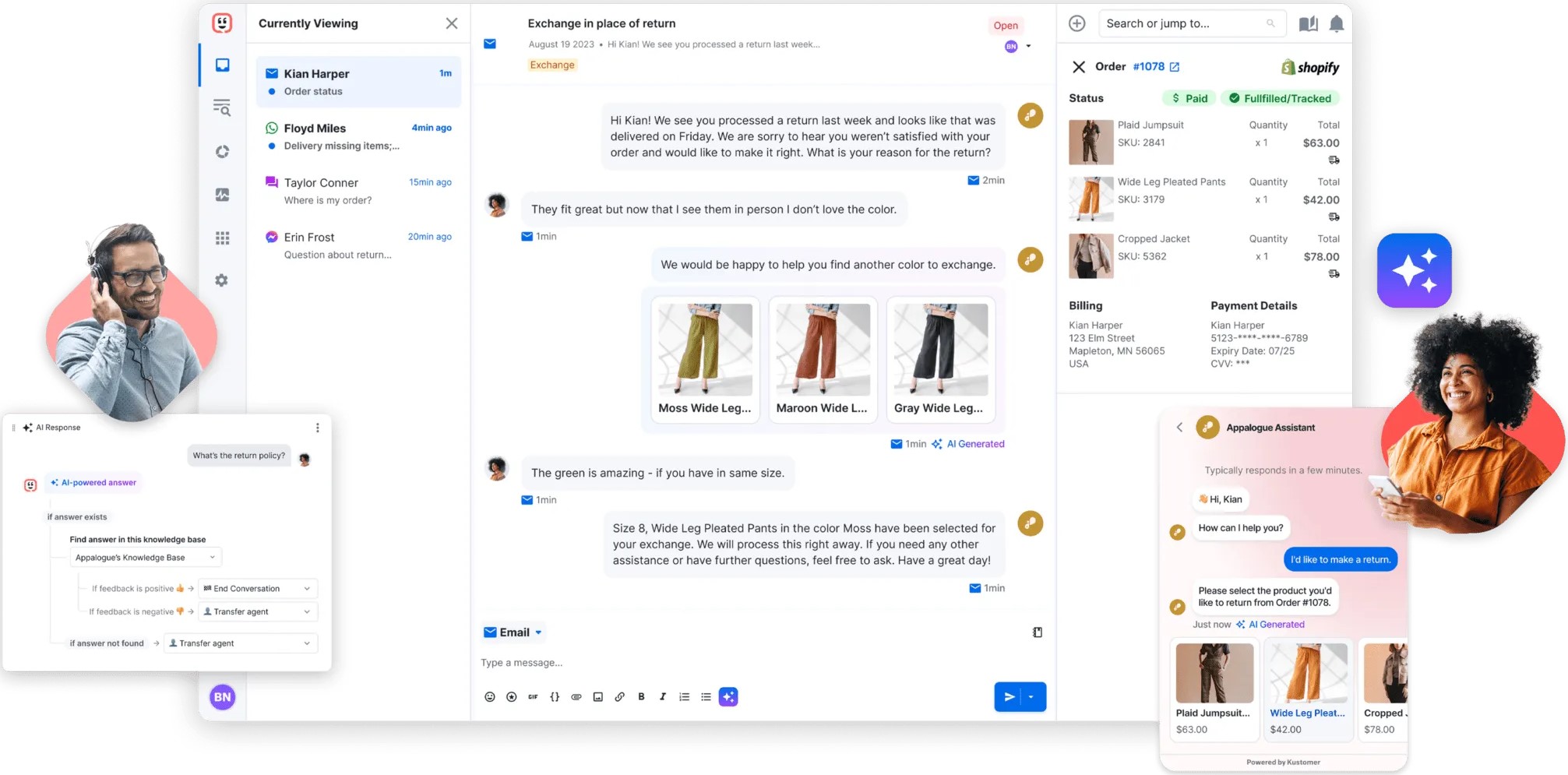
Seamless channel switching, also known as channel pivoting, allows customers to transition between different communication channels without losing context or having to repeat information. For example, a customer might start a conversation via live chat and then switch to a phone call without the need to re-explain their issue.
The feature ensures continuity in the customer journey, reducing frustration and saving time for both customers and agents. It reflects the natural way people communicate and adapts to their changing preferences or needs during an interaction.
4. Intelligent Routing
Intelligent routing uses advanced algorithms and rules to automatically direct customer inquiries to the most appropriate agent or department based on factors such as skill set, availability, and customer history.
The feature optimizes resource allocation, reduces wait times, and increases first-contact resolution rates. By ensuring that each query is handled by the right agent, intelligent routing improves efficiency of the support team and delivers quality of customer service. It leads to higher satisfaction rates and effective problem-solving.
5. Automated Responses and Chatbots
Leverage artificial intelligence enabled chatbots and automated responses to provide instant, 24/7 support for common queries and issues. These tools can handle a significant portion of customer interactions, from answering frequently asked questions to guiding users through simple troubleshooting steps.
Businesses can reduce response times, alleviate pressure on human agents, and provide round-the-clock support by automating routine tasks. Advanced chatbots can even learn from interactions, improving their responses over time and seamlessly escalating complex issues to human agents when necessary.
6. Real-time Analytics and Reporting
The advanced real-time analytics and reporting features provide businesses with instant insights into their customer service performance. These tools track key metrics such as response times, resolution rates, customer satisfaction scores, and channel usage in real-time.
Offering up-to-the-minute data and customizable reports enables managers to make informed decisions quickly, identify trends, and proactively address issues. Real-time analytics help businesses continuously optimize their customer service strategies and resource allocation for maximum efficiency and customer satisfaction.
7. Knowledge Base
A knowledge base is a centralized repository of information about products, services, and common issues, accessible to both customers and agents. It typically includes FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and detailed product information.
For customers, it enables self-service, allowing them to find answers quickly without contacting support. For agents, it serves as a comprehensive resource to assist in resolving complex issues. A well-maintained knowledge base can significantly reduce the volume of support tickets, improve response times, and ensure consistency in the information provided across all channels.
8. Customizable Workflows
Customizable workflows allow businesses to design and automate their unique customer service processes. The feature enables the creation of specific rules and sequences for handling different types of customer interactions or issues.
For example, a workflow might automatically escalate high-priority tickets or route specific inquiries to specialized teams. By tailoring workflows to their specific needs, businesses can streamline operations, ensure consistent service delivery, and adapt quickly to changing requirements or customer needs.
9. Collaboration Tools
Collaboration tools within omnichannel customer service software facilitate seamless communication and teamwork among support agents, supervisors, and other departments. These tools typically include features like internal chat, ticket sharing, and the ability to leave notes on customer profiles.
Enabling easy information sharing and collective problem-solving helps resolve complex issues more efficiently. They also promote knowledge transfer within the team, leading to improved service quality and faster resolution times.
10. Service Level Agreement (SLA) Management
SLA Management features help businesses track and meet their promised service standards. This tool typically includes the ability to set, monitor, and report on SLA metrics such as response times and resolution rates.
The feature can automatically prioritize and escalate tickets based on SLA requirements, ensuring that time-sensitive issues are addressed promptly. By helping businesses consistently meet their service commitments, SLA management tools contribute to improved customer satisfaction and trust.
11. Customizable Dashboards
Customizable dashboards provide a visual, at-a-glance overview of key performance indicators and metrics. Users can tailor these dashboards to display the most relevant information for their role or focus area.
For example, an agent might see their current ticket queue and performance metrics, while a manager might view team-wide statistics and trend analyses. These customizable views enable quick access to critical information, facilitating data-driven decision-making and allowing for rapid responses to changing service dynamics.