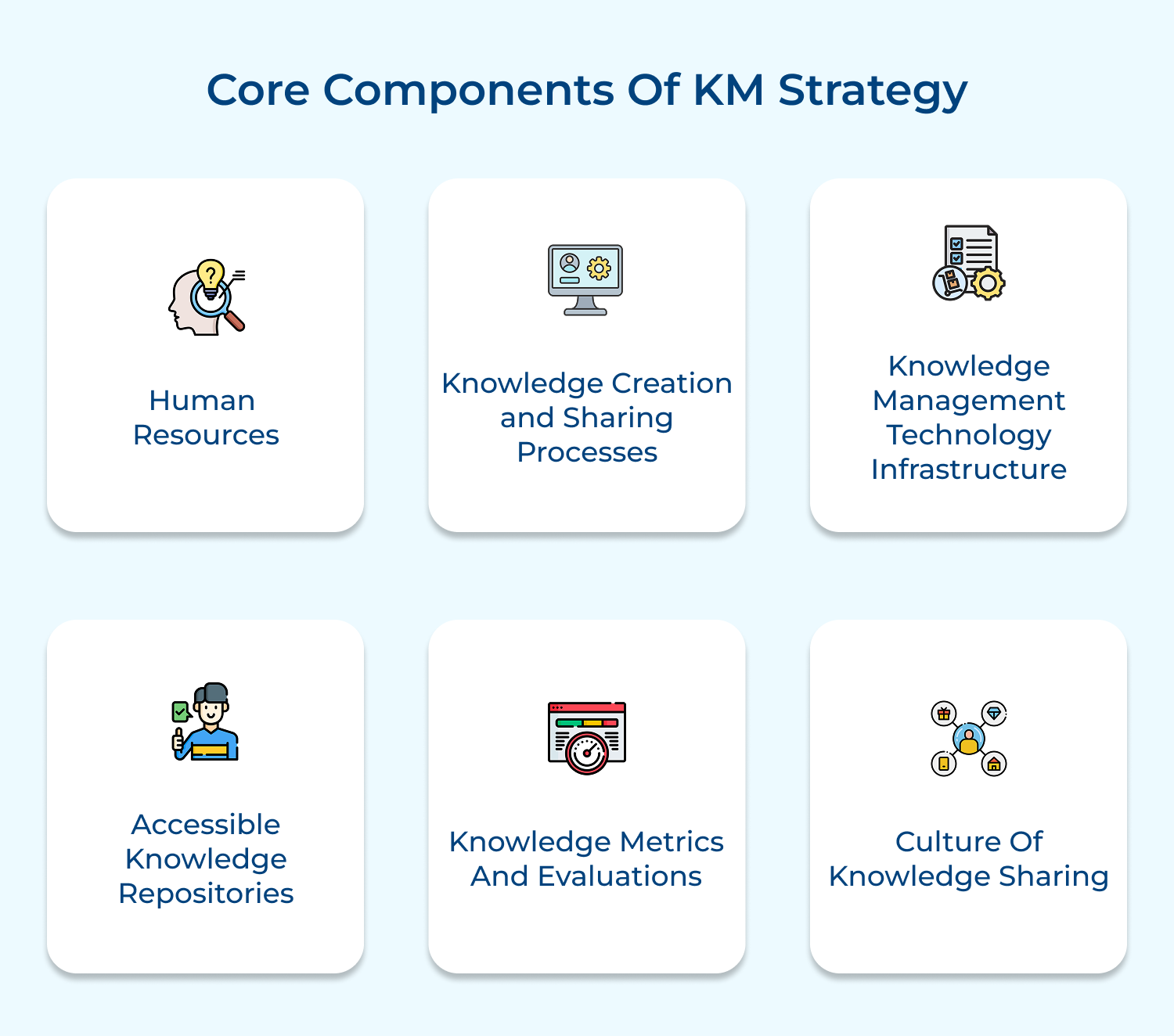
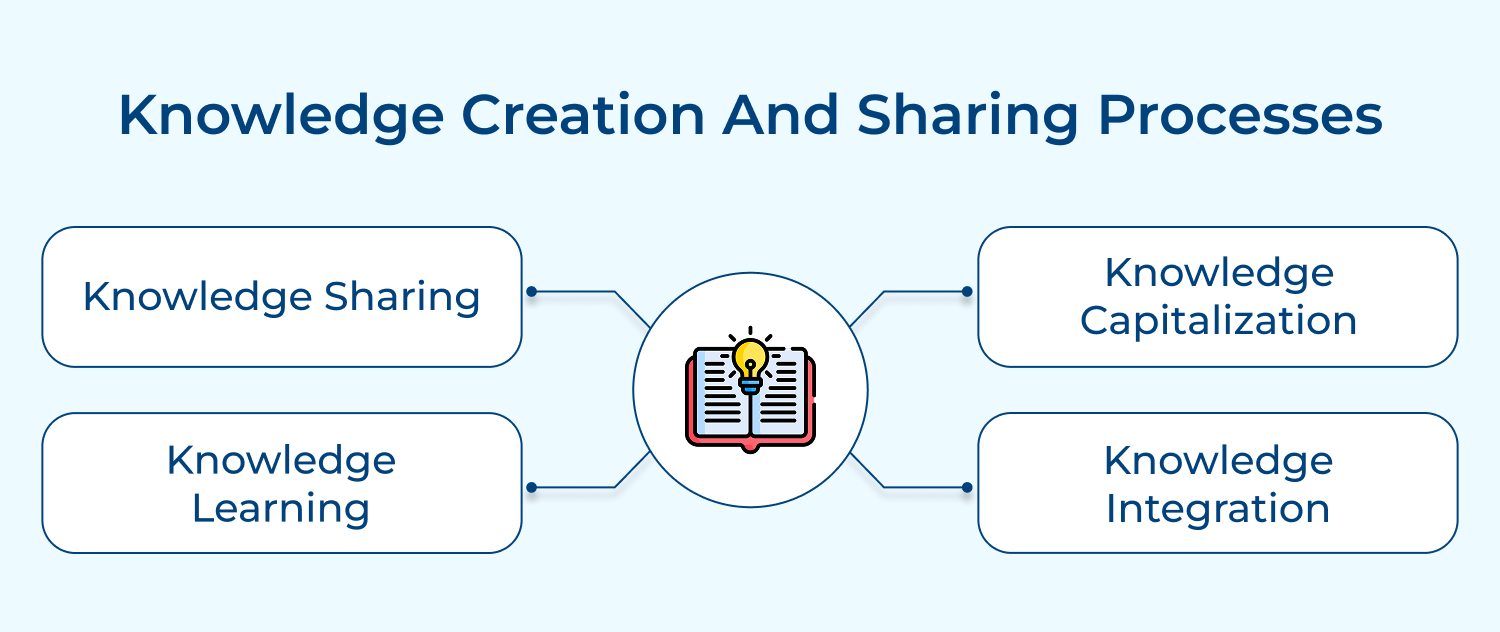
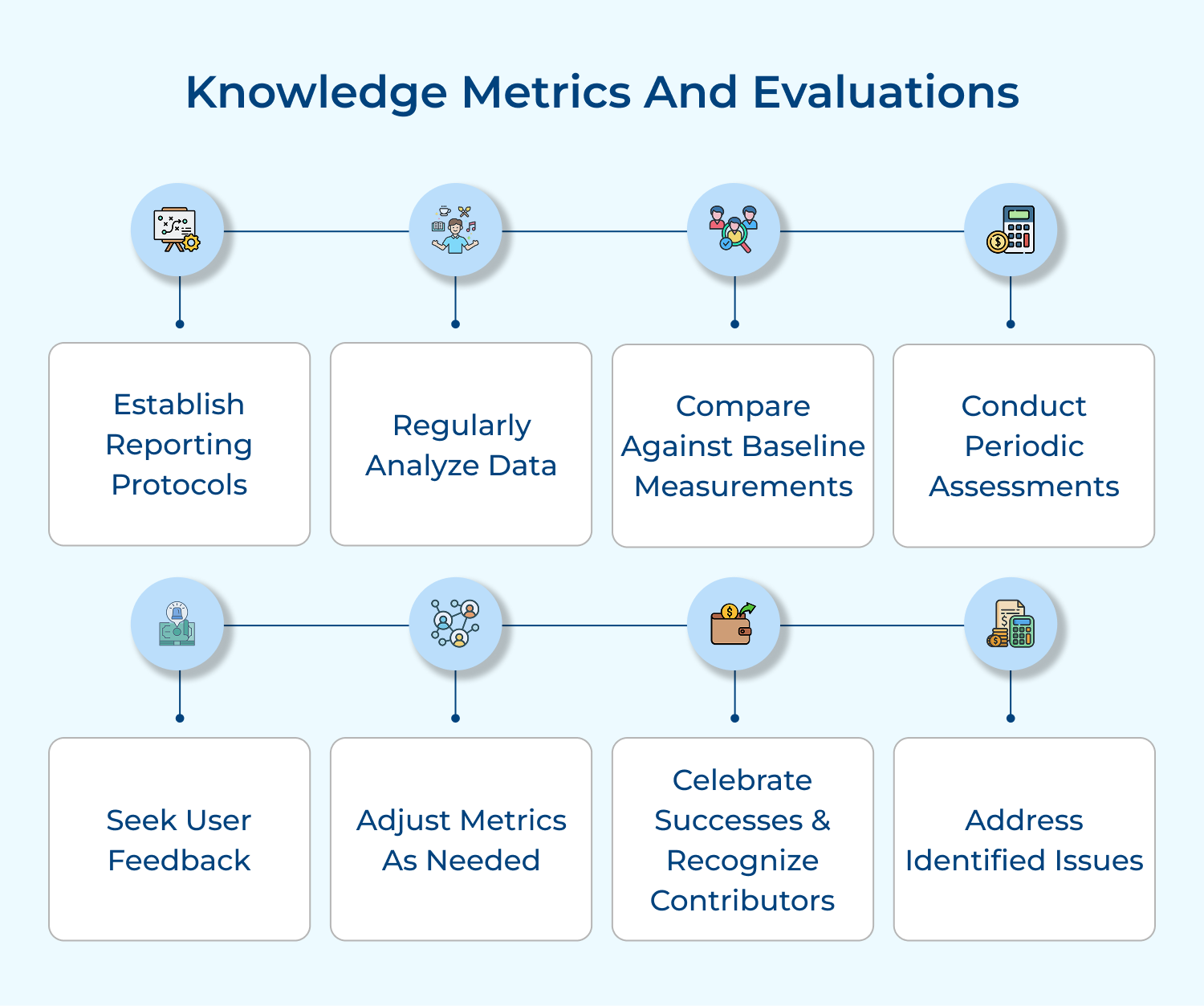
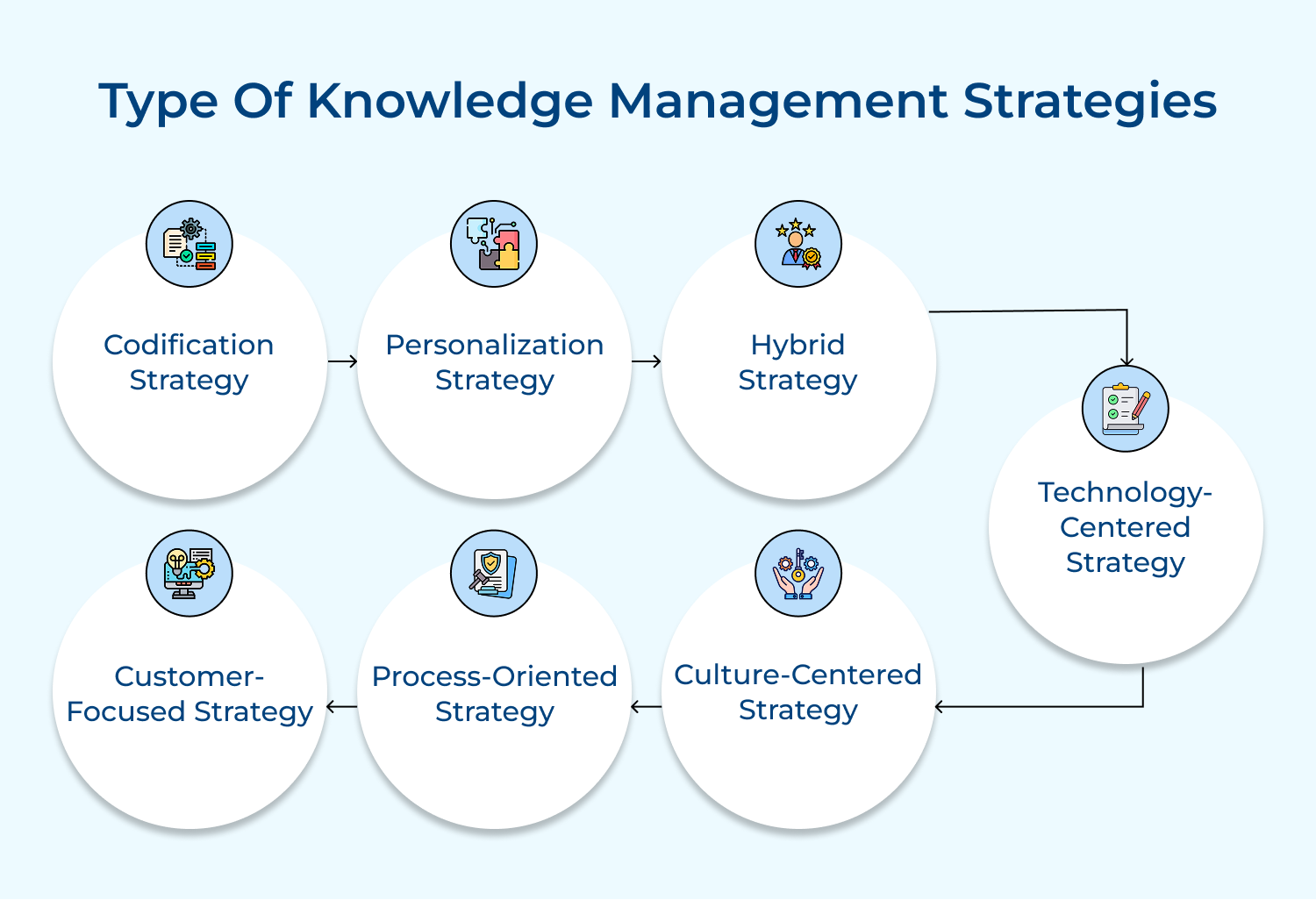
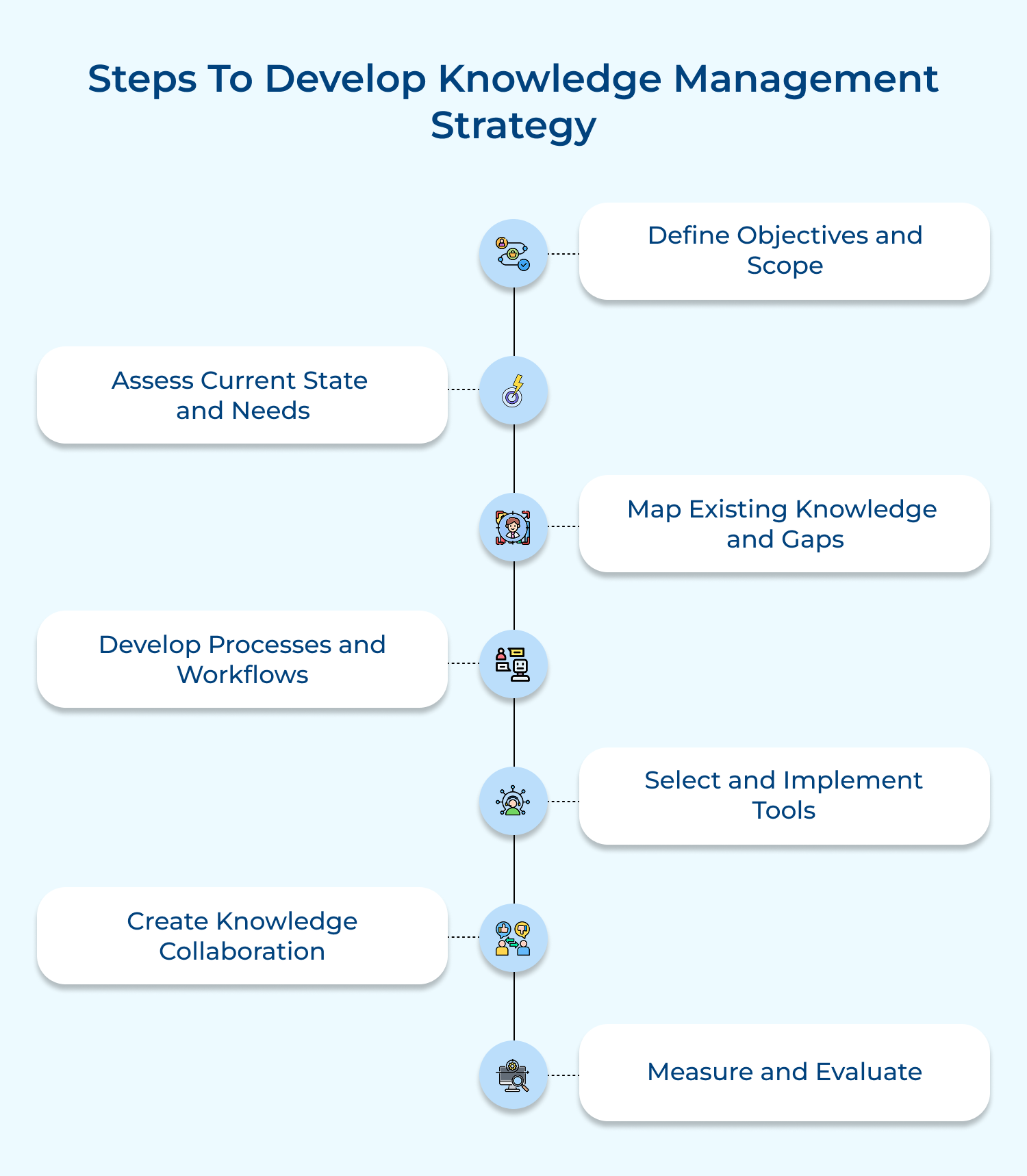
1. Codification strategy: The approach focuses on systematically capturing, storing and organizing explicit knowledge in a central repository. It involves creating detailed documentation, best practices guides and databases that employees can easily access.
Codification is particularly effective for organizations dealing with routine processes. It enables quick retrieval of knowledge, reduces duplication of efforts and ensures consistency in practices across the organization.
2. Personalization strategy: The strategy emphasizes person-to-person knowledge sharing, focusing on tacit knowledge transfer through direct interaction. It encourages networking, mentoring and collaborative problem-solving.
Personalization is ideal for companies dealing with unique, complex problems that require creative solutions. It encourages innovation and builds strong interpersonal relationships, but can be time-consuming and challenging to scale.
3. Hybrid strategy: The hybrid approach combines elements of both codification and personalization strategies. Organizations using a hybrid strategy implement systems to capture and store critical information while encouraging a culture of personal interaction and knowledge sharing.
The balanced approach allows for flexibility, catering to different types of knowledge and diverse organizational needs. It’s particularly effective for large, complex organizations with varied knowledge requirements across different departments or projects.
4. Technology-centered strategy: The strategy revolves around leveraging advanced technological solutions to manage knowledge. It involves implementing sophisticated knowledge management systems, artificial intelligence, data analytics and collaborative platforms.
The focus is on using technology to automate knowledge capture, improve access and enhance knowledge sharing. While this approach can significantly boost productivity and enable data-driven decision-making, it requires substantial investment in IT infrastructure and ongoing technical support.
5. Culture-centered strategy: The culture-centric approach prioritizes building an organizational culture that values and encourages knowledge sharing. It focuses on creating an environment where employees are motivated to share their expertise, learn from others and contribute to the collective knowledge base.
The strategy often involves implementing reward systems for knowledge sharing, encouraging open communication and promoting a learning mindset. While it can lead to sustainable knowledge management practices, it requires long-term commitment.
6. Process-oriented strategy: The strategy integrates knowledge management into core business processes. It involves mapping out key organizational processes and identifying critical knowledge points within these workflows.
The approach can lead to significant improvements in efficiency and decision-making quality. It requires a deep understanding of business processes and may necessitate process reengineering.
7. Customer-focused strategy: The customer-focused approach centers on capturing, managing and leveraging customer-related knowledge. It involves systematically collecting customer feedback, preferences and behavior patterns and using this information to improve products, services and customer experiences.
The strategy often employs CRM systems, customer analytics and feedback mechanisms. It can lead to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty but requires robust data management and analytics capabilities.